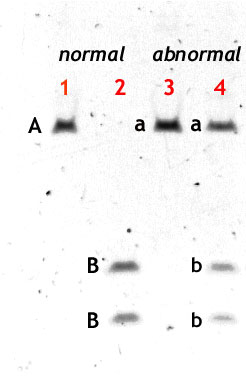
A restriction (or cutting) enzyme is then applied. If the PCR product is normal, this enzyme cuts it into two smaller pieces. On the gel, these show further down, as they are smaller (B and B).
Each sample application on the gel is called a lane and runs vertically downwards. Lane 1 shows a normal subject's DNA before cutting, and Lane2 shows his DNA after cutting.
Lane 3 shows an abnormal subject (he carries the R59W mutation for VP) before cutting. The typical PCR product is present (a). Lane 4 shows his DNA after cutting. Note the difference. Half his PCR product (made by the gene inherited from his normal parent) has behaved normally, and has cut into two smaller pieces,(b and b). However the half made by the mutated gene inherited from his affected parent has failed to cut, and remains at the start (a).
This is a quick and reliable test for the inheritance of a mutation, provided one knows just which mutation one is looking for.